THE HANSEATIC LEAGUE 1368 (E3)
xxxxxThe Hanseatic League of north European trading cities began in the 12th century, based at Visby in Sweden. By the end of the 13th century, Hamburg and Cologne had joined, and Lubeck had emerged as the leading centre. By 1377 the confederation consisted of some 200 cities and ports and held the monopoly of Baltic trade. It defended its members against pirates and nearby states -
 xxxxxThe Hanseatic League, a confederation of north European trading cities, had its beginnings in the twelfth century. The earliest association was based at Visby in Sweden and comprised some thirty cities, but in the 1260s, Hamburg and Lubeck established their own trading stations, and when these joined Cologne in 1282, the Baltic port of Lubeck emerged as the leading centre. By the end of this reign (1377) the organisation was at the height of its power, and included over 200 cities and towns, though the number did fluctuate. By now, trade extended to England and Flanders as well as to the Scandinavian countries and Russia.
xxxxxThe Hanseatic League, a confederation of north European trading cities, had its beginnings in the twelfth century. The earliest association was based at Visby in Sweden and comprised some thirty cities, but in the 1260s, Hamburg and Lubeck established their own trading stations, and when these joined Cologne in 1282, the Baltic port of Lubeck emerged as the leading centre. By the end of this reign (1377) the organisation was at the height of its power, and included over 200 cities and towns, though the number did fluctuate. By now, trade extended to England and Flanders as well as to the Scandinavian countries and Russia.
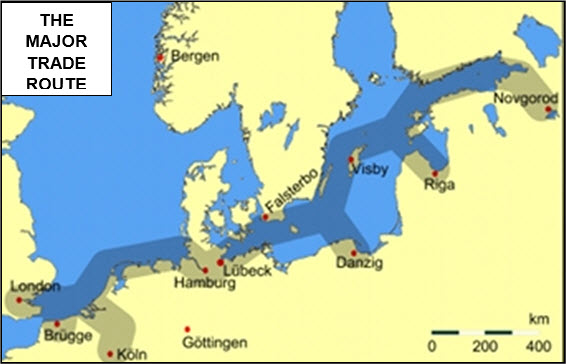 xxxxxThe strength of this Hanseatic League (Hanse is the German word for group or society) lay in its monopoly of the Baltic trade and its trading links with stations as far afield as London, Bruges, Bergen, and the Russian city of Novgorod. At this time, much of the trade was in cloth, timber, fish, tar, hemp, flax, furs, and metals like copper and iron.
xxxxxThe strength of this Hanseatic League (Hanse is the German word for group or society) lay in its monopoly of the Baltic trade and its trading links with stations as far afield as London, Bruges, Bergen, and the Russian city of Novgorod. At this time, much of the trade was in cloth, timber, fish, tar, hemp, flax, furs, and metals like copper and iron.
xxxxxThese associations arose from the merchants’ need for protection against attacks from local princes and pirates active in the Baltic and North seas. They sought help from their home towns -
xxxxxNor did the League shrink from military action. In 1361 when Denmark, anxious to break the league’s stranglehold on Baltic trade, seized Visby on the Swedish island of Gotland, the League went to war. The Danish army was decisively defeated in 1368, and by the Treaty of Stralsund two years later the Danes were obliged to recognise the supremacy of the League in the Baltic and to grant its merchants commercial privileges.
 xxxxxThe decline of the League was a slow one. From the fifteenth century onwards the old medieval trade routes gave way to new ones, notably those crossing from Europe to the Americas, and more powerful trading nations began to emerge like England and the Netherlands. In addition, the development of more rigidly defined national states made cross-
xxxxxThe decline of the League was a slow one. From the fifteenth century onwards the old medieval trade routes gave way to new ones, notably those crossing from Europe to the Americas, and more powerful trading nations began to emerge like England and the Netherlands. In addition, the development of more rigidly defined national states made cross-
xxxxxThus the League, once so powerful, simply faded away. By 1447 when the League held one of its periodic diets (meetings) only thirty-
Acknowledgements
Map (Scandinavia): licensed under Creative Commons. Author: Flo Beck -
E3-